One of the simplest inflation tilings is the chair tiling, which can be constructed in ![]() and higher dimensions. In
and higher dimensions. In ![]() the prototile is a cube from which a cube half its size in all three directions, so
the prototile is a cube from which a cube half its size in all three directions, so ![]() in volume, is cut out in one corner. The first order inflation tile may be built by capping the external corners of a central chair with
in volume, is cut out in one corner. The first order inflation tile may be built by capping the external corners of a central chair with ![]() additional chair prototiles. Its volume is
additional chair prototiles. Its volume is ![]() times the volume of a basic cube. (Fig.1)
times the volume of a basic cube. (Fig.1)
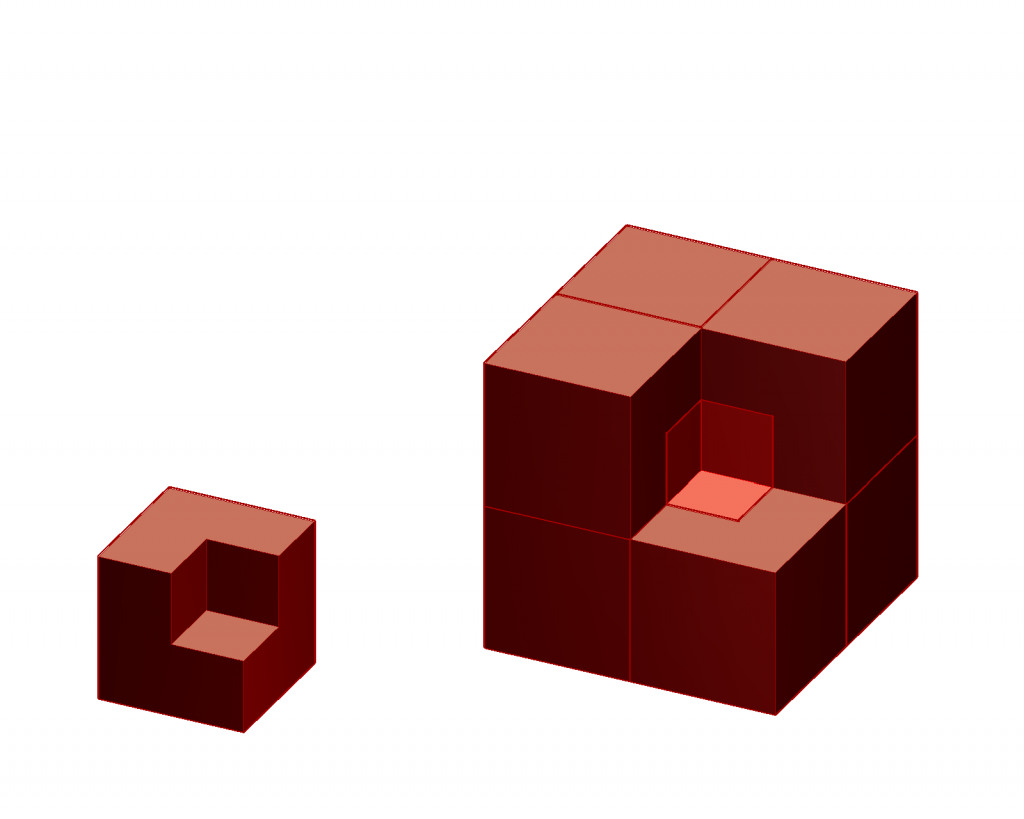
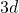 chair prototile and its first order substitution.
chair prototile and its first order substitution.Although all ![]() prototiles are identical, it is useful to distinguish central tiles and peripheral tiles. In a complete tiling the outside corners of the periferal tiles occupy points of a basic cubic lattice. The outside corners of the central tiles occupy some of the body centers of that lattice. An alternative description is that the central corners of the periferal tiles are situated at the body centers of the basic cubic lattice, i.e. one per unit cell. The internal corners of the central chair tiles on the other hand are at
prototiles are identical, it is useful to distinguish central tiles and peripheral tiles. In a complete tiling the outside corners of the periferal tiles occupy points of a basic cubic lattice. The outside corners of the central tiles occupy some of the body centers of that lattice. An alternative description is that the central corners of the periferal tiles are situated at the body centers of the basic cubic lattice, i.e. one per unit cell. The internal corners of the central chair tiles on the other hand are at ![]() of the basic cubic lattice points. More specific, the central chair tiles are at the body centers of an infinite set of superimposed simple cubic lattices having lattice parameters
of the basic cubic lattice points. More specific, the central chair tiles are at the body centers of an infinite set of superimposed simple cubic lattices having lattice parameters ![]() for
for ![]() to
to ![]() . The fraction of central chair tiles per lattice is
. The fraction of central chair tiles per lattice is ![]() ,
, ![]() , etc. or in general
, etc. or in general ![]() . The total fraction is
. The total fraction is ![]() , as it should.
, as it should.
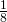 of center chair tiles is needed, the total fraction in the complete tiling being
of center chair tiles is needed, the total fraction in the complete tiling being 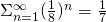
A generalization of this tiling was introduced by Chaim Goodman-Strauss (1999)(, European J. Combin., 20 (5): 385–395, doi:10.1006/eujc.1998.0282). By using two tiles, called the ![]() – and
– and ![]() -tiles he was able to force an aperiodic tiling by local matching rules.
-tiles he was able to force an aperiodic tiling by local matching rules.
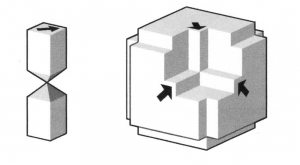
The ![]() -tile has a disconnected interior, i.e. as it were, two square pencils connected at their points. Alternative tiles may be constructed by combining the 3
-tile has a disconnected interior, i.e. as it were, two square pencils connected at their points. Alternative tiles may be constructed by combining the 3 ![]() -tiles to so-called cross-tiles or
-tiles to so-called cross-tiles or ![]() -tiles. Instead of only one
-tiles. Instead of only one ![]() -tile, two types of
-tile, two types of ![]() -tiles are needed, a cross without markings,
-tiles are needed, a cross without markings, ![]() and one with markings at the endpoints of one leg,
and one with markings at the endpoints of one leg, ![]() .
.
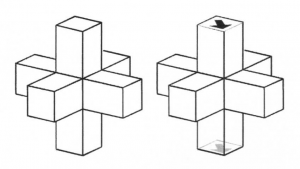
The ![]() -tiles are chair-like tiles, The
-tiles are chair-like tiles, The ![]() – or
– or ![]() -tiles are only needed to define the matching rules between the
-tiles are only needed to define the matching rules between the ![]() -tiles. Although not strictly necessary, it is also in this case convenient to distinguish two types of
-tiles. Although not strictly necessary, it is also in this case convenient to distinguish two types of ![]() -tiles, i.e. peripheral (
-tiles, i.e. peripheral (![]() ) and central (
) and central (![]() )-tiles. The
)-tiles. The ![]() -tiles only connect to
-tiles only connect to ![]() -tiles, the
-tiles, the ![]() -tiles only to one another. The
-tiles only to one another. The ![]() -tiles interconnect the unmarked legs of the
-tiles interconnect the unmarked legs of the ![]() -tiles. The ratio of
-tiles. The ratio of ![]() – and
– and ![]() -tiles is
-tiles is ![]() . To show this, we may cut up an
. To show this, we may cut up an ![]() -tile into 8 identical caps. By adding
-tile into 8 identical caps. By adding ![]() caps and removing the central one, an
caps and removing the central one, an ![]() -tile is converted into a chair tile, a total of 6 or
-tile is converted into a chair tile, a total of 6 or ![]() of an
of an ![]() -tile.
-tile.
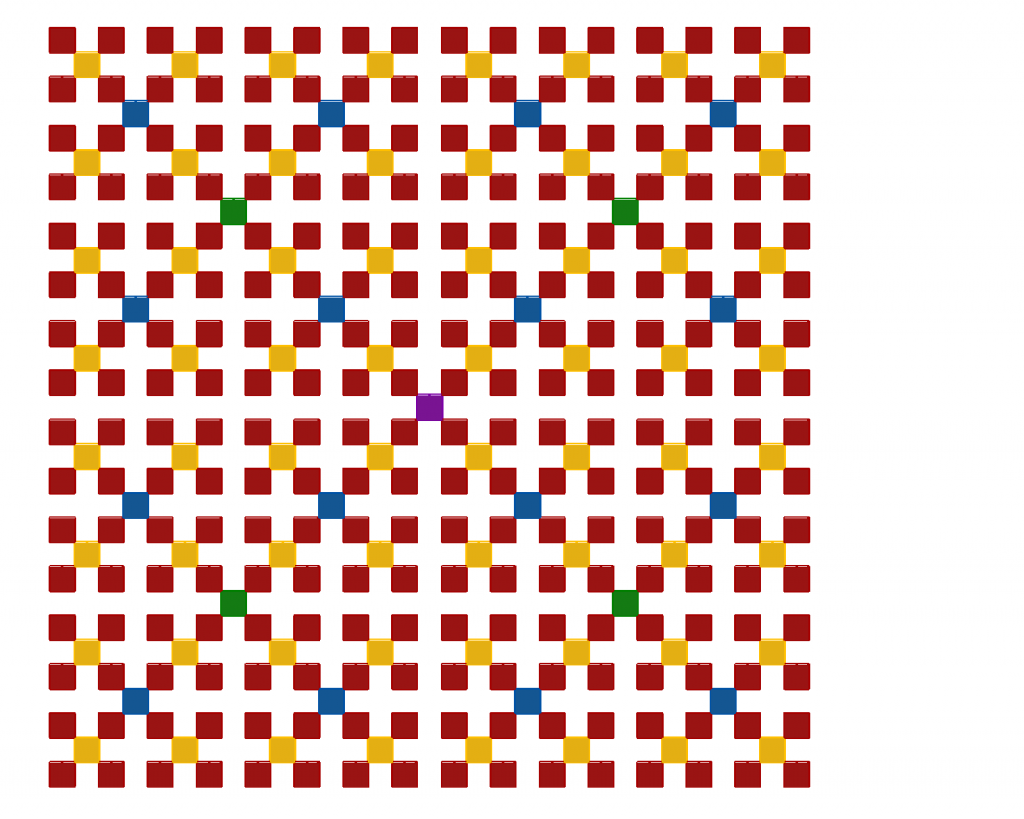
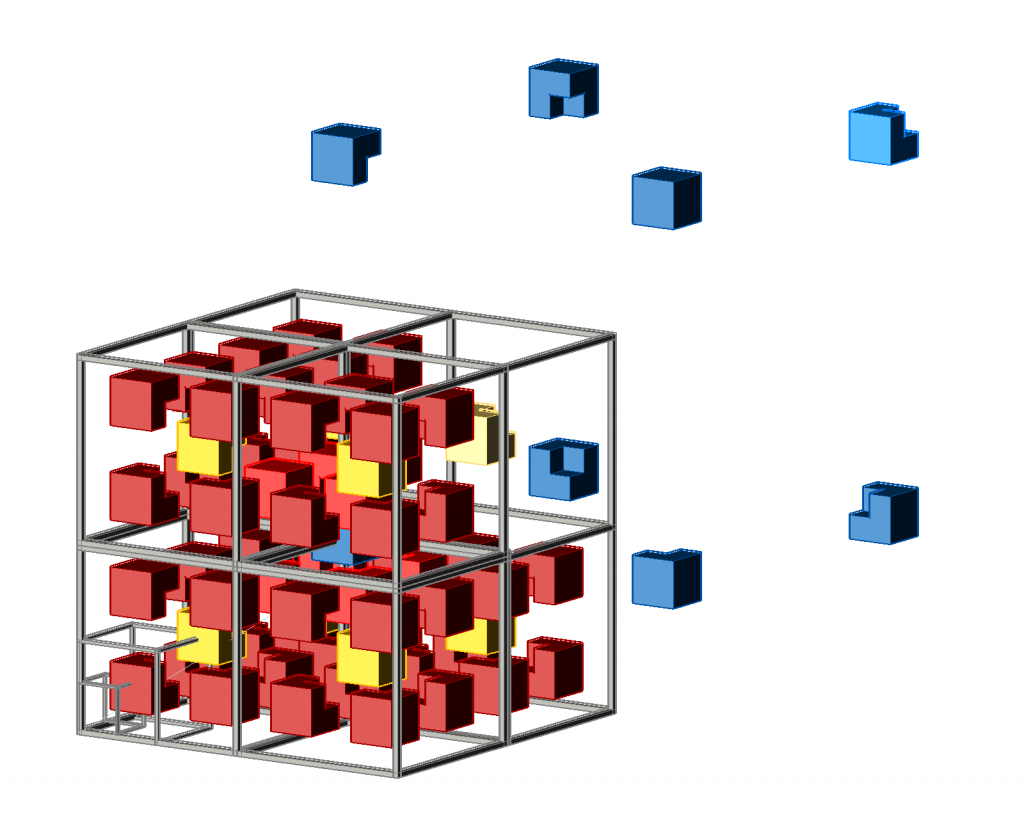
The ratio of marked and unmarked ![]() -tiles is 2. To prove this we consider the projection of the tiling in one of the main directions. As in the case of the chair tiling, the centers of the periferal
-tiles is 2. To prove this we consider the projection of the tiling in one of the main directions. As in the case of the chair tiling, the centers of the periferal ![]() -tiles occupy all body centers of a cubic lattice, whereas the central
-tiles occupy all body centers of a cubic lattice, whereas the central ![]() -tiles only occupy
-tiles only occupy ![]() of the basic lattice sites. In the projection of the tiling shown in fig.5 only the central
of the basic lattice sites. In the projection of the tiling shown in fig.5 only the central ![]() -tiles are shown. The marked
-tiles are shown. The marked ![]() -tiles connect the
-tiles connect the ![]() tiles. They form lines of legth
tiles. They form lines of legth ![]() ,
, ![]() to
to ![]() between succesive
between succesive ![]() tiles in the x,y and z direction. The fraction of lines connecting
tiles in the x,y and z direction. The fraction of lines connecting ![]() tiles perpenpendicular to the projection plane is equal to the fraction of colored squares, i.e the sum of
tiles perpenpendicular to the projection plane is equal to the fraction of colored squares, i.e the sum of ![]() (red),
(red), ![]() (yellow),
(yellow), ![]() (blue), etc., or
(blue), etc., or ![]() . Consequently, the fraction of lines of unmarked
. Consequently, the fraction of lines of unmarked ![]() -tiles in one direction is
-tiles in one direction is ![]() . The number of marked
. The number of marked ![]() -tiles along a line is the total number of basic cube lengths minus the number of
-tiles along a line is the total number of basic cube lengths minus the number of ![]() -tiles along the line. In a single direction, all the lines of marked
-tiles along the line. In a single direction, all the lines of marked ![]() -tiles connect all
-tiles connect all ![]() tiles. So, in all 3 directions, the fraction of marked
tiles. So, in all 3 directions, the fraction of marked ![]() -tiles is
-tiles is ![]() . This is equal to the fraction of marked crosses, because only one leg is marked. To build the marked crosses
. This is equal to the fraction of marked crosses, because only one leg is marked. To build the marked crosses ![]() of unmarked
of unmarked ![]() -tiles are needed and
-tiles are needed and ![]() unmarked
unmarked ![]() -tiles are left for the unmarked crosses. Consequently, the fraction of
-tiles are left for the unmarked crosses. Consequently, the fraction of ![]() is
is ![]() . In conclusion the ratio of
. In conclusion the ratio of ![]() ,
, ![]() -,
-, ![]() – and
– and ![]() -tiles is 7 : 1 : 4 : 2.
-tiles is 7 : 1 : 4 : 2.
In the Goodman-Strauss approach, the diameter of the legs of the ![]() -tile is an unspecified fraction
-tile is an unspecified fraction ![]() of the diameter of the
of the diameter of the ![]() -tile and the volumes of the
-tile and the volumes of the ![]() – and
– and ![]() -tile are
-tile are ![]() and
and ![]() respectively. For
respectively. For ![]() , the
, the ![]() – and
– and ![]() -tile have an identical cross shape and the volume of both is half the volume of a unit cube. We may transform the aperiodic Goodman-Strauss tiling into a tiling built out of identically shaped blocks by allowing the value of
-tile have an identical cross shape and the volume of both is half the volume of a unit cube. We may transform the aperiodic Goodman-Strauss tiling into a tiling built out of identically shaped blocks by allowing the value of ![]() to change to
to change to ![]() . We still may distinguish four types of tiles, now denoted by
. We still may distinguish four types of tiles, now denoted by ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and![]() .The
.The ![]() connect to each other in all three directions and may be positioned in the centers a basic cubic lattice. The
connect to each other in all three directions and may be positioned in the centers a basic cubic lattice. The ![]() tiles are connected to each other by X
tiles are connected to each other by X![]() -tiles and their centers positioned at the body centers of an infinite series of cubic lattices with lattice parameters
-tiles and their centers positioned at the body centers of an infinite series of cubic lattices with lattice parameters ![]() , which fit into holes between the periferal tiles. The remaining holes are fillled up with the unmarked X-tiles. We will now address the question , whether we can find matching rules for the identical X-tiles to force the aperiodic tiling obtained by a transformation of the Goodman-Strauss tiling.
, which fit into holes between the periferal tiles. The remaining holes are fillled up with the unmarked X-tiles. We will now address the question , whether we can find matching rules for the identical X-tiles to force the aperiodic tiling obtained by a transformation of the Goodman-Strauss tiling.
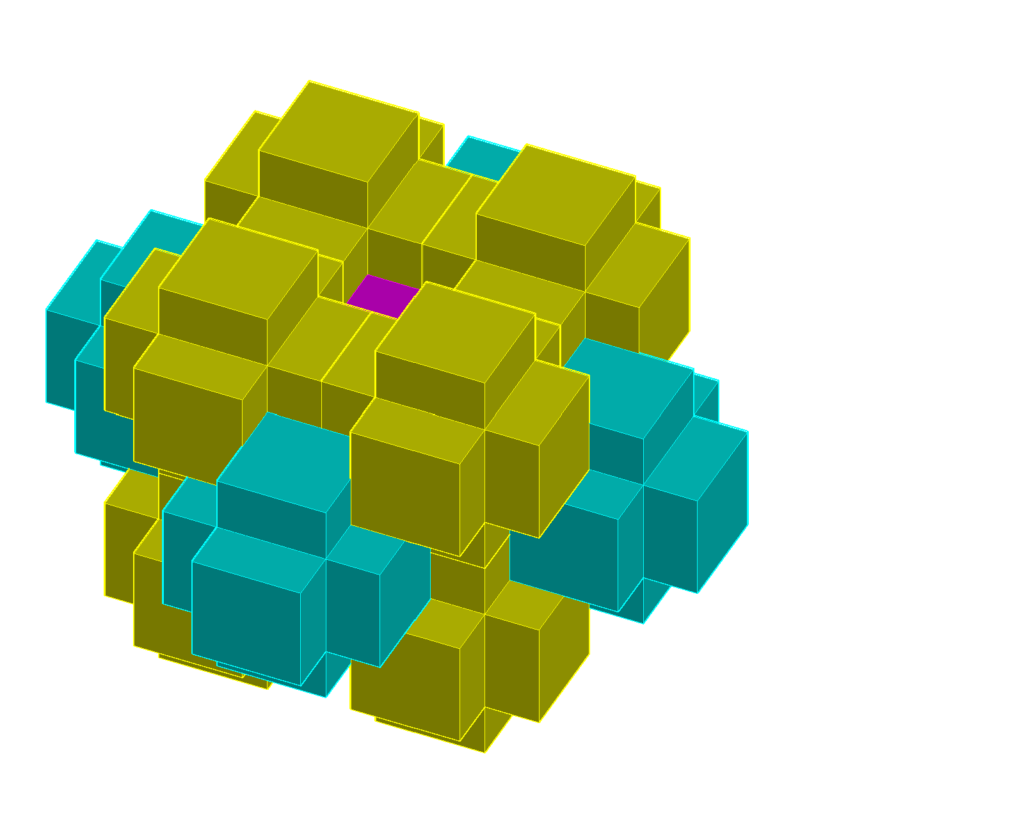
An important difference is that the chair tiles have a trigonal C![]() symmetry and the X-tiles are objects with an octahedral O
symmetry and the X-tiles are objects with an octahedral O![]() symmetry. A consequence is that the directionality of the markings on the
symmetry. A consequence is that the directionality of the markings on the ![]() -tiles is becoming useless and the black arrows in GS may be replaced by colored faces. The matching rules are now that a) the
-tiles is becoming useless and the black arrows in GS may be replaced by colored faces. The matching rules are now that a) the ![]() tiles only connect to each other through the small square faces, and b) the
tiles only connect to each other through the small square faces, and b) the ![]() tiles never are connected directly to each other, but only through one or more
tiles never are connected directly to each other, but only through one or more ![]() tiles. But these rules are not sufficient to force an aperiodic tiling. The
tiles. But these rules are not sufficient to force an aperiodic tiling. The ![]() sublattice tiling is perfectly periodic due to rule a). Also rule b) may be used to build a periodic lattice with a lattice constant twice as large as the width of
sublattice tiling is perfectly periodic due to rule a). Also rule b) may be used to build a periodic lattice with a lattice constant twice as large as the width of ![]() -tile , two
-tile , two ![]() tiles occuping the corner and body center positions, and the
tiles occuping the corner and body center positions, and the ![]() tiles the face center and edge positions. In order to get the Goodman-Strauss like tiling, an additional building principle (not matching rule) would be to put the
tiles the face center and edge positions. In order to get the Goodman-Strauss like tiling, an additional building principle (not matching rule) would be to put the ![]() tiles on a periodic simple cubic
tiles on a periodic simple cubic ![]() lattice with lattice constant 1 and the
lattice with lattice constant 1 and the ![]() tiles successively on basic cubic lattices with lattice constants
tiles successively on basic cubic lattices with lattice constants ![]() ,
, ![]() to
to ![]() . The
. The ![]() tiles are connected to each other along the edges of thes lattices using
tiles are connected to each other along the edges of thes lattices using ![]() tiles. The origin of the
tiles. The origin of the ![]() lattice with lattice constant
lattice with lattice constant ![]() is positioned at the body center of the lattice with lattice constant
is positioned at the body center of the lattice with lattice constant ![]() . Finally, the remaining holes are filled up with
. Finally, the remaining holes are filled up with ![]() tiles.
tiles.